ARTICLES
Tao
By adam
Aggregation difficulties
- content tailored to each user
- filter item with privacy checks for each user
- impossible to aggregate and filter when content is crated
- resolve data dependencies and privacy check each time content is viewed
- pull vs push social graph?
- extreme read demands on graph data store
Memcache
- rapid deployment
- data mapping
- cache invalidation
- client code that is deployed frequently
- created abstractions for graphcs
- r/w objects (nodes)
- associations (edges)
- direct access to MySQL deprecated for graph data tyles
Tao
- service
- implements objects
- and association model
- motivation
- encapsulating failures in the PHP API
- access graph easily from non-PHP serivces
- problems with lookaside cache architecture
Inefficient edge lists
- KV cache is not good semantic fit for lists of edges
- queries must fetch the entire edge list
- list support would help
- make changes to single edge causes entire list to be reloaded
- requires coordination of incremental updates to cached lists
- queries must fetch the entire edge list
Distributed control logic
- L-A $ control logic is run on clients
- clients don’t communicate with each other
- increases the number of failure modes
- difficult to avoid thundering herds
- Nishtala et al. leases as a general solution
- For graphs (objects and associations)
- API allows one to move control logic into the cache itself
Expensive read after write consistency
- FB uses asynchronous master/slave replication for MySQL
- problem for caches using a replica
- write to master
- take time to appear in replica
- Nishtala remote makers track keys that are known to be stale forwarding reads to keys to master region
- restricting data model to objects and associations
- update replica’s cache at write time
- use graph semantics to interpret cache maintenance messages from
concurrent updates
- provides read-after-write consistency for all clients that share a cache without requiring inter-regional communication
- problem for caches using a replica
Functional requirements
- access to nodes and edges
- constantly changing graph
- multiple region support
- heavy read optimized
- favors efficiency and availability over consistency
- tolerate some staleness
- fine grained customized content from highly interconnected data
Data model
- Alice uses her mobile phone to record her visit to GG bridge with Bob.
- Cathy makes a comment
- David likes the comment
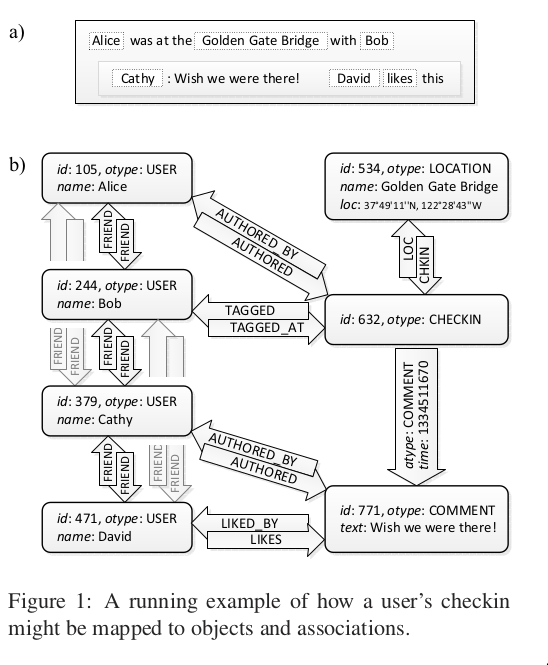
- application servers query events underlying nodes and edges every time it is rendered
- fine-grained privacy control means each user sees a different view of the same
event
- nodes and edges can be reused by views
- but aggregated content and results from privacy checks cannot
Objects and associations
- 64-bit id
- associations source object, association type (atype), destination object
- at most one association of a given type between any two objects
- objects and associations may contain data
- per-type schema
- possible keys, value type, and default value
- 32-bit time field - generic application-assigned integer
- Object: (id) -> (otype, (key->value)*)
- Assoc: (id1,atype,id2) -> (time, (key->value)*)
Actions and objects
- two actions comment and like
- comment resulted in an object
- like resulted in an association
- associations naturally model actions that
- can happen at most once
- record state transitions
- repeatable actions better represented as objects
- associations are directed, but often have a inverse edges
- COMMENT doesn’t have inverse edge to CHECKIN
- application doesn’t need it
- once a CHECKIN id is known, you only need to traverse outbound edges
- discovering the CHECKIN object requires inbound edges
- COMMENT doesn’t have inverse edge to CHECKIN
- schema for objects and associations describe only the data contained in
instances
- do not impose any restriction on edge types that can connect to a node
- do not import any restriction on node types that can terminate an edges
- why is there no object type?
- wouldn’t you have a different schema depending on the object type?
- atype for AUTHOR is the same for CHECKIN and for COMMENT
Object API
- Create (New)
- Read
- Update
- can be applied to a subset of the fields
- Delete
- no CAS
Association API
- Symmetric FRIEND
- Asymmetric AUTHORED vs AUTHORED_BY
- support for keeping associations in sync with inverse
- atype can be configured with inverse type
- symmetric association are their own inverse
- write:
- assoc_add(id1, atype, id2, time, (k->v)*)
- assoc_delete(id1, atype, id2)
- assoc_change_type(id1, atype, id2, newtype)
Association query API
- query needs to have an origination object and a association type
- CHECKIN object and tagged users and comments
- creation-time locality
- focuses on recent items
- if Alice is famous, only the most recent comments will be rendered
- association lists
- list of all associations with a particular id1 and atype arranged in descending order by time field
- Association List: (id1, atype) -> [a_1000, a_999, a_998, …. a_old]
- queries
- assoc_get(id1, atype, id2set, high?, low?)
- assoc_count(id1, atype)
- assoc_range(id1, atype, pos, list)
- assoc_time_range(id1, atype, high, low, limit)
- per-type upper bound (6000)
- limit for an association query
- if you want more you need to issue multiple queries with pos or high
- 50 most recent comments from Alice’s checkin
- assoc_range(632, COMMENT, 0, 50)
- how many checking at the GG bridge?
- assoc_count(534, CHECKIN)
Tao architecture
Cache
- tier
- multiple cache servers
- leader/follower tiers
- one leader multiple follower tiers
- one leader (coordinator) per database
- in single tier configuration
- each tier contains set of cache servers that can respond to any query
- large single tier is problematic
- prone to hot spots
- quadratic growth in all-to-all connections
- followers communicate with leader
- clients only communicate with follower tier (and neighboring ones/failure)
- writes for same key go to same leader shard
- followers must be notified of updates from other follower tiers
- leader enqueues invalidation messages to each corresponding follower
- follower issuing write is update synchronously on reply from leader
- version number allows it to be ignored if arrives late
- cache only contiguous prefixes of association lists
- invalidating an association might truncate the list and discard many edges
- instead leader sends a refill message to notify followers about as association write
- follower that cached the association with refill request triggers a query to leader to update its stale association list
- follower issuing write is update synchronously on reply from leader
- leader enqueues invalidation messages to each corresponding follower
- leaders serialize concurrent writes
- also protects database from thundering herds
- it does not issue concurrent overlapping queries to DB
- also limts the max number of pending queries to a shard
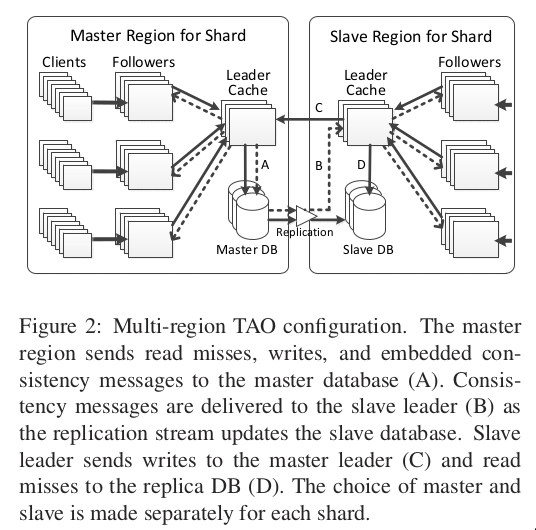
Multi-region
- follower tiers can be thousands of miles apart
- read misses by followers are 25x as frequent as writes
- writes go to master
- read misses serviced locally
- propagation of update notifications are asynchronous
- too expensive to provide full replicas in every data center
- choose data center locations that are clustered into a few regions
- intra-region latency small (1ms)
- sufficient to store one complete copy of the social graph per region
- choose data center locations that are clustered into a few regions
- followers behave identically in all regions
- forward misses and writes to local region’s leader tier
- leader query local region’s db regardless whether it is a master/slave
- read latency is independent of inter-region latency
- writes are forwarded by the local leader to the leader with master
- we prefer to locate all of the master DBs in a single region ???
- when inverse association is mastered in a different region
- must traverse inter-reiong link to forward the inverse write
- when inverse association is mastered in a different region
- invalidations and refill messages are delivered immediately after a
transaction has been replicated to a slave database
- prevents cache inconsistencies
- use same pipeline for delivery of invalidations as memcache
- forward writes from local leader
- local leader will update its cache with fresh value
- local slave DB doesn’t have updates yet
- followers receive two invalidates or refills from the write
- one sent with write succeeds
- one sent when the write’s transaction is replicated
- local leader will update its cache with fresh value
Optimization
- Slab allocator
- manages slabs of equal size items
- Thread-safe hash table
- LRU eviction among items of equal size
- Dynamic slab rebalancer keeps LRU eviction ages similar across slabs
- Slab item can hold one node or one edge list
- RAM partitioned into arenas
- arena selected by object or association type
- allows lifetime of important types
- for small fixed-size items like association counts
- memory overhead of pointer for bucket items in main hash table become significant
- use direct-mapped 8-way associated cache that require no pointers
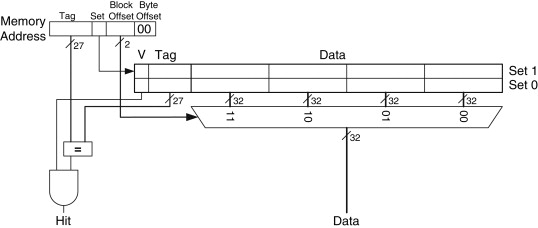
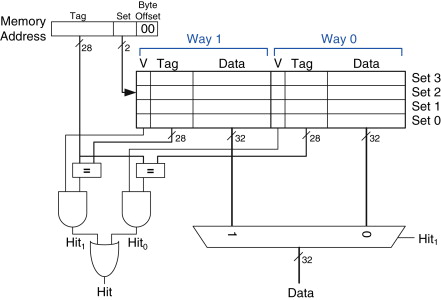
- LRU slides entries down
- map each atype to 16 bit value
- id1,atype : id was 64-bit or 8 bytes, if atype is 16 bits or 2 bytes then total is 10 bytes. Why is there a 32 bit count in 14 bytes. 32 bit count is 4 bytes, so maybe total count would be 10+4 bytes 10 bytes if there is no id2 (negative entry) in 10 bytes, since no count.
MySQL rows
- all fields of an object are serialized into a single ‘data’ column
- allow us to store objects of different types within the same table
- associations support range queries, so have index based on id1,atype,time
- association counts are stored in a separate table
Hot spots
- shard clones
- follower for a hot shard is cloned
- place high hit objects in a small client-side cache
- when follower responds to a query for hot item
- includes the object or association’s access rate
- if rate exceeds a certain threshold, tao client caches the data and version, version number allows follower to omit data in replies if the data has not changed
- access rate can also be used to throttle client requests for very hot objects
High-degree objects 5.4
- many objects have 6000 associations with the same atype
- assoc_get(id1,id2) no edges between
- for high-degree objects these queries will always go to the DB
- because id2 could be in the uncached tail of the association list!
- use assoc_count to choose query direction
- checking the inverse edge id2 -> id1 is equivalent
- if both ends are high-degree - use application domain knowledge
- since an edge to a node can only be created after a node has been created then
you can limit id2 search to time > its creation time
- if an edge order than the id2’s creation time exists in the association list then you know there is no edge to id2
Consistency 6.1
- goal is availability and performance
- eventual consistency model - ok to send stale data
- replication lag is less than 1 sec!
- within single tier provides read-after-write consistency
- updates cache with locally written values
- master leader returns a changeset when write is successful
- changeset propagated to slave leader to follower tier that originated query
- inverse associations have to send to 2 shards
- slave leader and follower must forward the changeset to id2’s shard
- changeset cannot be written right away
- follower cache may be stale if refill or invalidate from another update
has not been delivered
- use version number
- globally increment during each update
- follower can invalidate its local copy if the changeset’s version is stale
- in slave regions vulnerable to race condition
- cache eviction and storage server update propagation
- slave storage server holds older version than what was cached by caching server
- possible for the post-changeset entry to be evicted from cache then reloaded from the database
- client observes value go back in time
- this occurs if it takes longer for the slave region storage to receive update than update for the cached item to be evicted from cached
- cache eviction and storage server update propagation
- use version number
- follower cache may be stale if refill or invalidate from another update
has not been delivered
- updates cache with locally written values
Failure dectection 6.2
network failures
- each server aborts requests to destinations it can no longer reach
- tao routes around failures
database failures
- when slave db is down
- cache misses are redirected to TAO leaders in the region hosting the DB master
- cache consistency messages can’t be delivered by the primary mech ?
- additional binlog tailer is run on the master database which refills and invalidates are delivered inter-regionally
leader cache failure
- followers reroute to database
- write are rerouted to random member of the leader’s tier
- replacement leader performs write and associated actions
- like modify inverse association
- sending invalidation to followers
- enqueues asynchronous invalidation to the original leader
- async invalidates recorded on coordinating node and inserted into the replication stream until the leader becomes available
- used when leader comes back up its consistency needs to be restored
- replacement leader performs write and associated actions
refill and invalidation failures
- follower not reachable
- leader queues the message to disk and delivers at a later time
- if leader fails
- there is a bulk invalidation of all objects and associations
follower failures
- follower in other tiers share the responsibility of serving the failed host’s shards
- each tao client has a primary and a backup follower tier
- failing over between different tiers may cause read-after-write violation
- read reaches the failover target before the write’s refill or invalidate
Multi-tenancy 7
- amortize operational cost
- share excess capacity
- enable applications to link to existing data
- important for objects
- allows entire 64-bit id space to be handled uniformly without an extra step to resolve the otype
Region 7
- follower tiers spread across several geographical regions
- each region has
- one complete set of databases
- one leader cache tier
- two or more follower tiers
- 1e9 reads 1e6 writes / s